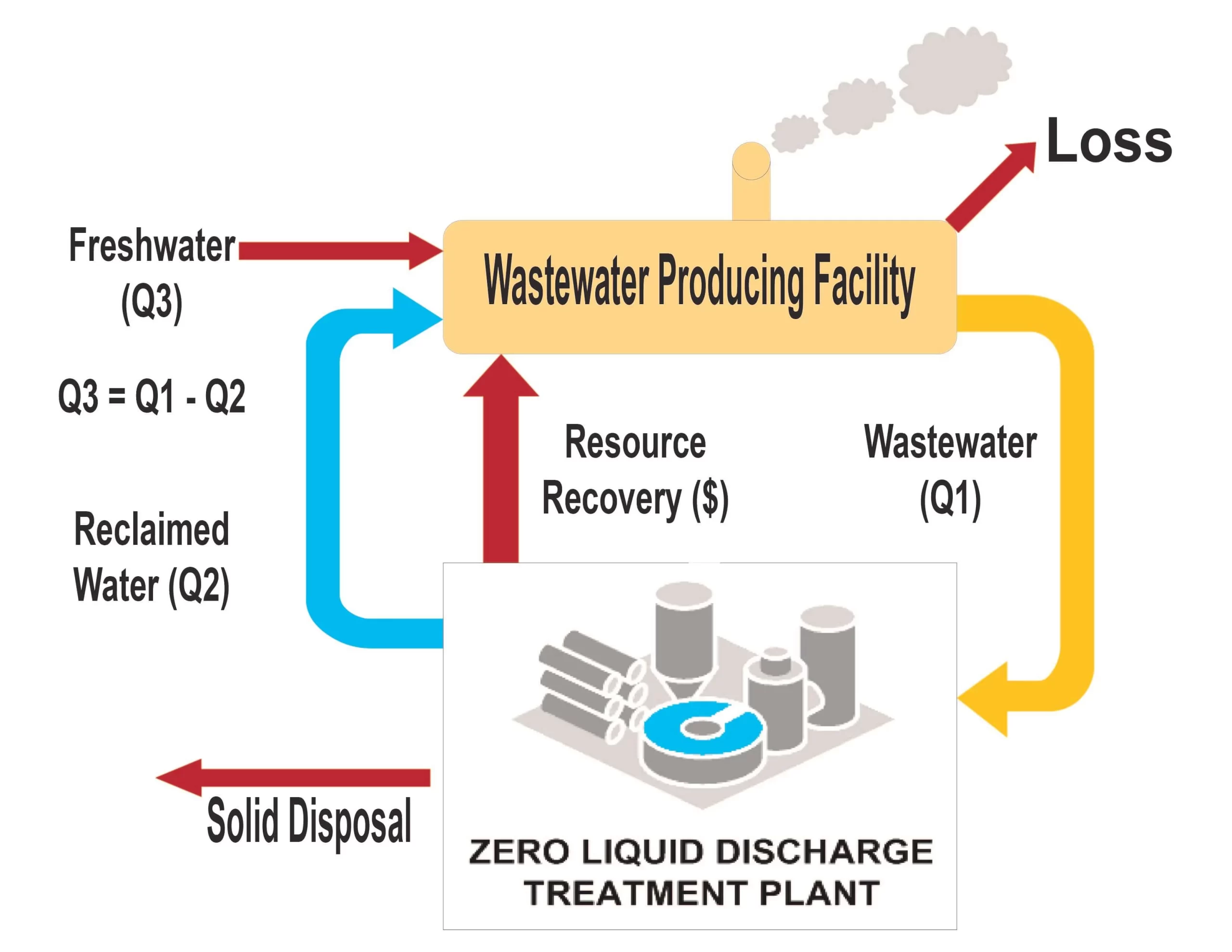
Zero liquid discharge (ZLD)
Zero liquid discharge can be defined as an efficient wastewater management system that ensures no discharge of industrial wastewater into the environment. It involves wastewater treatment process of recycling followed by recovery and reuse for industrial purposes.
Key Features of an Efficient Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) System
🔁 Adaptability to flow and contamination fluctuations — Effectively manages variable waste volumes and pollutant concentrations
🧪 Flexible chemical handling — Easily accommodates shifts in chemical composition during treatment
💧 High recovery rate — Recovers up to 95% of liquid waste
🧂 Resource reclamation — Capable of retrieving and treating valuable by-products such as salts and brine
🗑️ Solid waste output — Produces dry solid cake suitable for safe disposal
♻️ Sustainability-focused — Reduces environmental impact through maximum recovery and minimal liquid discharge
Contents of Zero Liquid Discharge
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) operates as a closed-loop system designed to eliminate liquid waste discharge entirely. It utilizes a combination of advanced treatment methods, including:
🌡️ Thermal processes such as evaporation and crystallization
💧 Membrane-based technologies like reverse osmosis, electrodialysis, forward osmosis, and membrane distillation
A standard ZLD system typically comprises:
⚗️ Physicochemical and biological pretreatment to remove initial contaminants
🚰 Membrane filtration stages, primarily Reverse Osmosis (RO), to concentrate waste streams
🔥 Thermal units including evaporators and crystallizers for final separation and solidification
Benefits of Zero Liquid Discharge
Benefits of a Typical Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) System
🔁 Eliminates wastewater discharge by recycling and reusing treated streams
💸 Reduces operational costs through efficient recovery of water and valuable salts
🌍 Supports sustainable industrial practices with minimal ecological impact
🌿 Contributes to environmental restoration by minimizing pollutant release
🚜 Preserves water resources, enabling reuse in agriculture, domestic utilities, and other operations
🧱 Utilizes by-product sludge as input for applications such as cement manufacturing
Working of a Typical ZLD Treatment System
Although specific processes vary, a typical ZLD system includes the following processes as shown in figure 1.
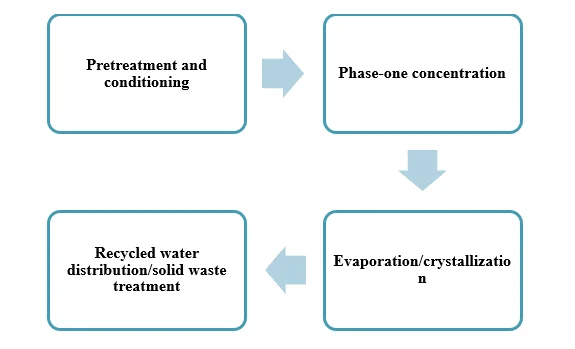
1.Pre-treatment and Conditioning
Pretreatment: A Critical Phase in Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) Systems
The pretreatment step plays a vital role in safeguarding downstream processes from fouling and scaling.
💧 Filtration and precipitation eliminate simpler contaminants that may interfere with advanced treatment stages.
⚗️ Clarification removes metals, hardness, and silica through controlled precipitation.
🧪 Coagulation, utilizing widely accepted agents like alum and polyaluminum chloride, effectively captures bulk suspended solids.
🔄 After coagulation, the water flows into the flocculation chamber, where fine particles aggregate into flocs.
⬇️ The mixture then enters a gravity settler for slow settling, allowing separation of flocculated material.
The nature of influent wastewater—particularly its metal and silica content—determines the necessity for additional chemical treatments or reactors. For a successful and efficient ZLD operation, careful attention to the pretreatment phase is essential.
2.Phase One Concentration
The pretreated water is moved through the reverse osmosis step where majority of the dissolved solids are captured. On the other hand brine concentrators also reduce the dissolved solids but they can handle high salt concentration of brine as compared to RO. Electrodialysis is another membrane process that can be used at this stage of ZLD. All these processes combined can concentrate the stream and remove up to 80% of the water content.
3.Evaporation/Crystallization
After the completion of concentration step, solid is generated in this step. Dissolved oxygen, carbon dioxide and other non-condensable gases can be released during this step through deaeration. The leftover waste is then subjected to crystallizer where all the water is evaporated and boiled until water impurities crystallize out and filtered as solid.
4.Recycled Water Distribution / Solid Waste Management
The treated water can be reused in the industry provided it is purified enough to be reused in the processes. The solid waste generated will be subjected to dewatering process to yield a solid cake.
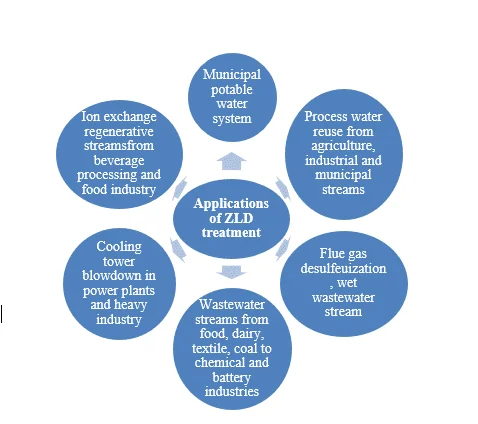
Implementation of ZLD Around the Globe
Geographical location plays an important role in the implementation of ZLD in different countries around the world. At present majority of ZLD systems in the world are functional in USA. Most of the systems are operating in power generation sector treating cooling tower blowdown and flue gas desulfurization (FGD) wastewater.
China, having water intensive power plants owned by largest state own agencies in water scarce areas, has considered the implementation of ZLD systems as a sustainable option. In addition to this, boom in coal to chemical plants also require ZLD systems for the preservation of water and ecosystem.
Due to the escalating water scarcity issue in India, all the textile plants generating wastewater greater than 25 m3 were required to install ZLD systems under the water conservation policies of the Indian government. India has also extended the application to different industries including beverage, food, pharmaceutical, power, textile, chemical and steel.
Pakistan being a developing country has a great scope for ZLD to cater for its water scarcity issue and conserve the water resources and environment. Industrial sector including textile, food, beverages, power generation and petrochemical are main areas for ZLD application. However, factors such as capital, operation cost and land need full consideration for efficient and full-scale application in the country.
Pioneering water sustainability, the integration of Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD), the eco-friendly efficacy of Biocleaner, and the precision of Real-Time Monitoring converge to redefine wastewater management, ensuring responsible practices and optimal purification outcomes.
