Chlorination System
Chlorine systems are effective in removing bacteria and viruses from water sources. These systems are relatively inexpensive that is why it remains so popular.
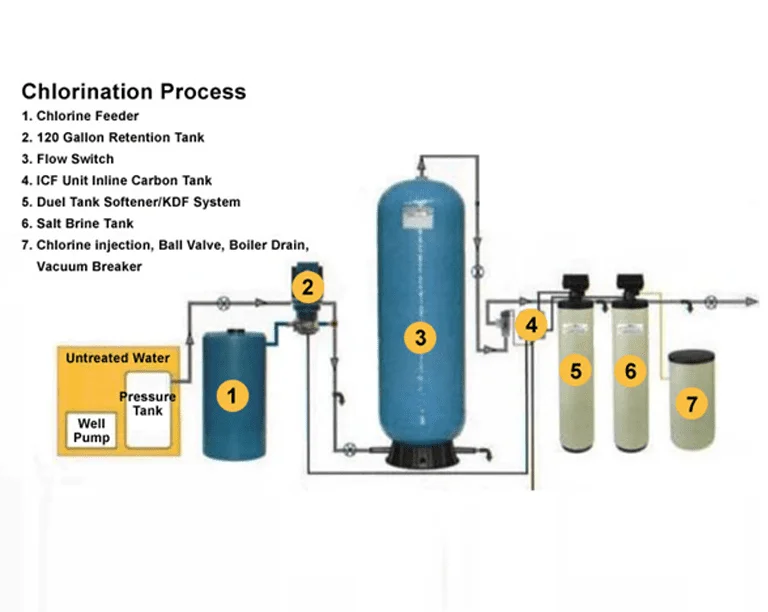
WCSP typical chlorination system consists of a chemical feed pump which meters precise amounts of diluted chlorine into the incoming water stream. This chlorinated water is then contained in a reservoir called a ‘contact tank’. These tanks varied in their capacity. Chlorine requires a minimum 20 minute contact time for effect. After this point of operation, remove excess of chlorine for maintain taste and odor.
Silent features
- Kill harmful coliform and E.coli bacteria
- Eliminate sulfur (hydrogen sulfide) odors
- Oxidize iron, manganese for easier filtration
- Low cost and effective
Types of Chlorination Systems
Gas Chlorination
Gas chlorination involves introducing chlorine gas into water, providing an efficient method for large-scale disinfection. This method is widely used in municipal water treatment facilities.
Liquid Chlorination
Liquid chlorination employs liquid chlorine solutions to treat water. This versatile method allows for precise dosage control and is commonly used in various industrial applications.
Tablet Chlorination
Tablet chlorination utilizes chlorine tablets that dissolve in water, releasing chlorine gradually. This method is often employed in smaller-scale water treatment applications and swimming pools.
How Chlorination Works
Chlorination operates through a chemical reaction between chlorine and water. Chlorine effectively oxidizes and eliminates pathogenic microorganisms, disrupting their cellular structure and rendering them harmless.
The disinfection process is a crucial step in water treatment, preventing the spread of waterborne diseases. Chlorine’s ability to react with a wide range of contaminants makes it a versatile and effective disinfectant.
Advantages of Chlorination
Chlorination offers several advantages in water treatment. Its effectiveness in pathogen elimination, including bacteria and viruses, makes it a trusted method for safeguarding public health. Additionally, its widespread application in various water treatment processes highlights its versatility and reliability.
Safety of Chlorinated Water
While chlorinated water is generally safe to drink, excessive chlorine levels can pose health risks. Regulatory bodies carefully monitor and control chlorine levels in treated water to ensure they meet safety standards. Continuous testing and adjustments are made to maintain an optimal balance between disinfection and safety.
Dosage Determination in Chlorination
The dosage of chlorine in a chlorination system is determined by factors such as water volume, quality, and the desired level of disinfection. Water treatment professionals adhere to established guidelines to calculate the appropriate chlorine dosage, ensuring effective disinfection without compromising safety.
Alternatives to Chlorine
In addition to chlorine, other water disinfection methods exist. UV treatment, ozonation, and chloramine disinfection are alternatives that offer unique advantages depending on specific treatment requirements and environmental considerations.
Maintenance of Chlorination Systems
Regular maintenance of chlorination systems is essential for optimal performance. This includes monitoring chlorine levels, inspecting equipment for wear and tear, and conducting routine calibrations. These measures contribute to the reliability and longevity of chlorination systems.
Chlorination in Swimming Pools
Chlorination is a common practice in maintaining water quality in swimming pools. It effectively eliminates bacteria and prevents the growth of algae, creating a safe and enjoyable environment for swimmers.
Environmental Impact of Chlorination
While chlorine is effective in water disinfection, concerns exist about the environmental impact of its byproducts. Efforts are underway to mitigate these effects, including the development of more sustainable chlorination methods.
Chlorination in Industrial Settings
Chlorination finds application in industrial processes, contributing to water treatment and ensuring the quality of water used in various manufacturing and production activities. Specific challenges in industrial settings require tailored solutions to optimize chlorination effectiveness.
Future Trends in Chlorination Technology
Advances in chlorination technology are ongoing, with a focus on developing more sustainable and eco-friendly approaches. Innovations aim to improve efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and address emerging challenges in water treatment.
Community Water Treatment Programs
Chlorination plays a vital role in community water treatment programs, ensuring the delivery of safe water to households. The public health impact of such programs is significant, contributing to the reduction of waterborne diseases in communities.
Chlorination and Waterborne Diseases
Chlorination has been instrumental in preventing the spread of waterborne diseases. Historical examples showcase its success in reducing the incidence of diseases such as cholera and typhoid. Ongoing efforts continue to leverage chlorination for public health benefits.
Conclusion
In conclusion, chlorination systems are indispensable in the quest for safe and clean water. From municipal water treatment to swimming pool maintenance, chlorination’s versatility and effectiveness make it a cornerstone of water disinfection. As we look to the future, advancements in chlorination technology will likely bring about even more sustainable and efficient water treatment methods. We also provide many systems like Ozone Generator and Filling Machines for water safety.
chlorination system is a water treatment method that involves the introduction of chlorine into water to disinfect it and eliminate bacteria, viruses, and other harmful microorganisms.
The chlorination system works by adding chlorine, typically in the form of gas, liquid, or solid tablets, to water. Chlorine reacts with organic and inorganic substances in the water, destroying pathogens and preventing the spread of waterborne diseases.
Chlorine is a powerful disinfectant that effectively kills bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms in water. It is widely used in water treatment to ensure the safety of drinking water and to prevent the spread of waterborne diseases.
Chlorination systems come in various forms, including gas chlorination, liquid chlorination, and tablet chlorination. Each type has its advantages and is suitable for different applications.
Yes, chlorinated water is generally safe to drink within regulated limits. The chlorine levels in treated water are carefully monitored to ensure they meet safety standards and do not pose health risks.
Excessive chlorine levels in drinking water can be harmful. However, water treatment facilities carefully control and monitor chlorine levels to ensure they are within safe limits according to regulatory standards.
The dosage of chlorine in a chlorination system is determined based on factors such as the water volume, quality, and the target level of disinfection. Water treatment professionals use established guidelines to calculate the appropriate chlorine dosage.
Yes, there are alternative water disinfection methods such as UV treatment, ozonation, and chloramine disinfection. The choice of method depends on various factors including water quality, cost, and specific treatment requirements.
Regular maintenance of a chlorination system involves monitoring chlorine levels, checking equipment for wear and tear, and ensuring proper functioning of the system. Routine inspections and calibration are essential for optimal performance.
Yes, chlorination systems are commonly used for disinfecting swimming pool water. They help maintain water quality by eliminating bacteria and preventing the growth of algae, ensuring a safe and enjoyable swimming environment.
