Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation has emerged as an innovative and versatile solution for treating a wide range of industrial and municipal wastewater. By integrating electrochemical reactions with traditional coagulation and flocculation processes, it offers a highly efficient and chemical-free treatment method.
This technology stands out for its environmental compatibility, low operational costs, and minimal sludge generation. Its adaptability across industries—such as textile, metal finishing, food processing, and pharmaceutical manufacturing—makes it a reliable choice for diverse effluent treatment needs.
With its strong performance in removing heavy metals, suspended solids, oils, and other contaminants, Electrocoagulation is a forward-thinking solution in modern wastewater management.
Working Principal
Electrocoagulation (EC) is an advanced and versatile water treatment process that integrates electrochemical reactions with natural coagulation and flocculation to remove a wide range of contaminants. As a promising solution for industrial wastewater treatment in Pakistan, EC continues to gain traction for its efficiency and operational simplicity. The WCSP team has launched multiple EC pilot projects across various industries to evaluate its environmental performance and cost-effectiveness, reinforcing its potential as a sustainable treatment technology.
The core process of electrocoagulation involves:
Dissolution of metal cations at the anode:
M → M⁺ + ne⁻ (1)Generation of hydroxyl ions (OH⁻) and hydrogen gas at the cathode:
2H₂O (l) → OH⁻ + H₂ (g) (2)
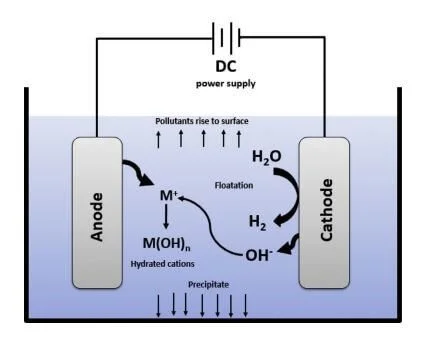
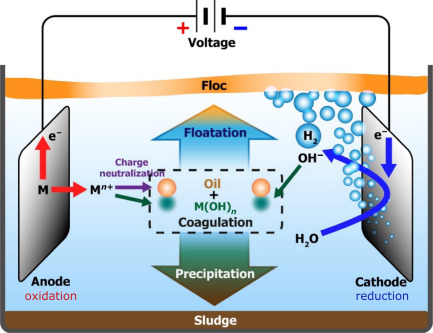
A standard EC unit consists of an electrolytic cell equipped with metal electrodes (typically iron or aluminum) immersed in wastewater and connected to an external DC power source. These non-toxic and readily available metals serve as sacrificial anodes that release metal cations upon electrical activation.
The released Fe²⁺ and Al³⁺ cations destabilize colloidal particles through the formation of monomeric and polymeric hydroxo complexes. These complexes exhibit strong adsorption properties, facilitating the aggregation of pollutants into removable flocs.
Figure 1 illustrates the layout of a typical EC cell.
Experience Reliable Water TreatmentSolutions for Any Project
Feed gas preparatory:
The feed gas can consist of either dry air or concentrated oxygen. Dry air is air that has been dried to a dew point of -60°F or lower.
Concentrated oxygen refers to a purified gas containing at least 90% oxygen, with all moisture removed to ensure optimal performance in specialized applications such as electrocoagulation (EC) wastewater treatment, industrial effluent treatment, and electrochemical coagulation. This process utilizes iron and aluminum electrodes, offering an eco-friendly solution for water treatment and wastewater purification. WCSP’s EC system supports sustainable wastewater treatment through pilot projects and advanced electrochemical water purification technologies in Pakistan.
Power input:
The primary power demand arises from the conversion of oxygen into ozone. Supplementary power needs encompass the preparation of feed gas, the ozone contact process, as well as the power necessary for control, instrumentation, and monitoring facilities.
3.Ozone generating device:
Ozone is typically generated on-site for disinfection purposes using a corona discharge method. The ozone is produced by applying high voltage between closely spaced electrodes, using either air or concentrated oxygen as the source.
The high-energy corona, generated through the process mentioned above, separates one oxygen molecule, which then combines with two other oxygen molecules to form an ozone molecule.
Using ambient air as the feed gas, this method generates an ozone concentration ranging from 1–3% by weight. When pure oxygen is used instead, the resulting ozone concentration increases significantly—typically between 3–10% by weight.
4.Contact basin:
The most critical process during use of ozone as the disinfectant is the proper mixing of ozone in the water. Two types of systems are used for this purpose i.e. ozone transfer via bubble diffusion or venture.
Bubble diffusion refers to the ozone transferred by diffusers. The diffusers create small bubbles of ozone in water. As the bubble rises, the gas at the edge of the bubbles will transfer into the water.
Venturi injection system work by forcing water through the conical body. This process creates a pressure differential between inlet and outlet ports resulting in a vacuum inside the injector body.
This vacuum effect enables the swift induction of ozone through the designated suction port, ensuring efficient mixing within the system.
Wastewater treatment with Electrocoagulation, ZLD, Biocleaner
Uniting the precision of Electrocoagulation, the sustainability of Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD), and the ecological strength of Biocleaner technologies forms a powerful trio in modern wastewater treatment—delivering high-efficiency purification with minimal ecological footprint.
Advantages
Key Advantages of Electrocoagulation (EC) Technology
No secondary pollution risk — EC operates without chemical additives, preserving environmental integrity.
⚙️ Simplified operation — The process is straightforward and supports complete automation.
High-quality output — Treated wastewater is clear, odorless, and colorless.
Stable, easily filterable flocs — EC-generated flocs are larger and more stable than those from chemical coagulation, allowing efficient separation.
Effective contaminant removal — Toxic substances and heavy metals are reduced to non-detectable levels.
Reduced sludge production — Compared to chemical processes, EC generates significantly less sludge.
Enhanced colloid removal — Applied current accelerates particle collisions, facilitating coagulation of the smallest colloidal particles.
