Distillation Plant
Distillation is a highly effective water purification process that works by separating pure water from contaminants—not by filtering out impurities, but by removing the water itself through controlled evaporation and condensation cycles. The result is distilled water, which is virtually free from dissolved solids, salts, heavy metals, and other impurities.Because of its ability to deliver exceptionally high-purity water, distillation is widely regarded as one of the most reliable methods for water treatment and recycling. It is particularly ideal for sensitive applications, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing, laboratory use, medical equipment sterilization, and battery-grade water production.
Silent Features
Key Benefits
- Ultra-Pure Water Quality – Ideal for critical applications requiring high purity
- Extended System Lifespan – Minimizes scaling and corrosion, enhancing equipment durability
- Comprehensive Contaminant Removal – Effectively eliminates both suspended and dissolved solids


Benefits of Using a Water Distillation Plant
Advantages of a Water Distillation Plant
Water distillation offers unmatched purity, producing water free from harmful contaminants. Distilled water is perfect for safe drinking and a variety of industrial and high-precision applications, ensuring reliable performance and hygiene in all uses.
Future Trends in Distillation Technology
The future of distillation technology holds promise in adopting sustainable practices and integrating artificial intelligence. These advancements aim to further enhance efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and ensure long-term viability.
Conclusion: Advancing Sustainability Through Distillation
Distillation plants remain a cornerstone in the field of separation technologies. Their continued evolution, versatile applications, and sophisticated designs highlight their critical role across numerous industries.
Enhance your sustainability goals with our integrated water recycling solutions—featuring advanced systems like Distillation Plants, Water Softening Units, and Chlorination Systems—designed for efficient, reliable, and eco-friendly water management.
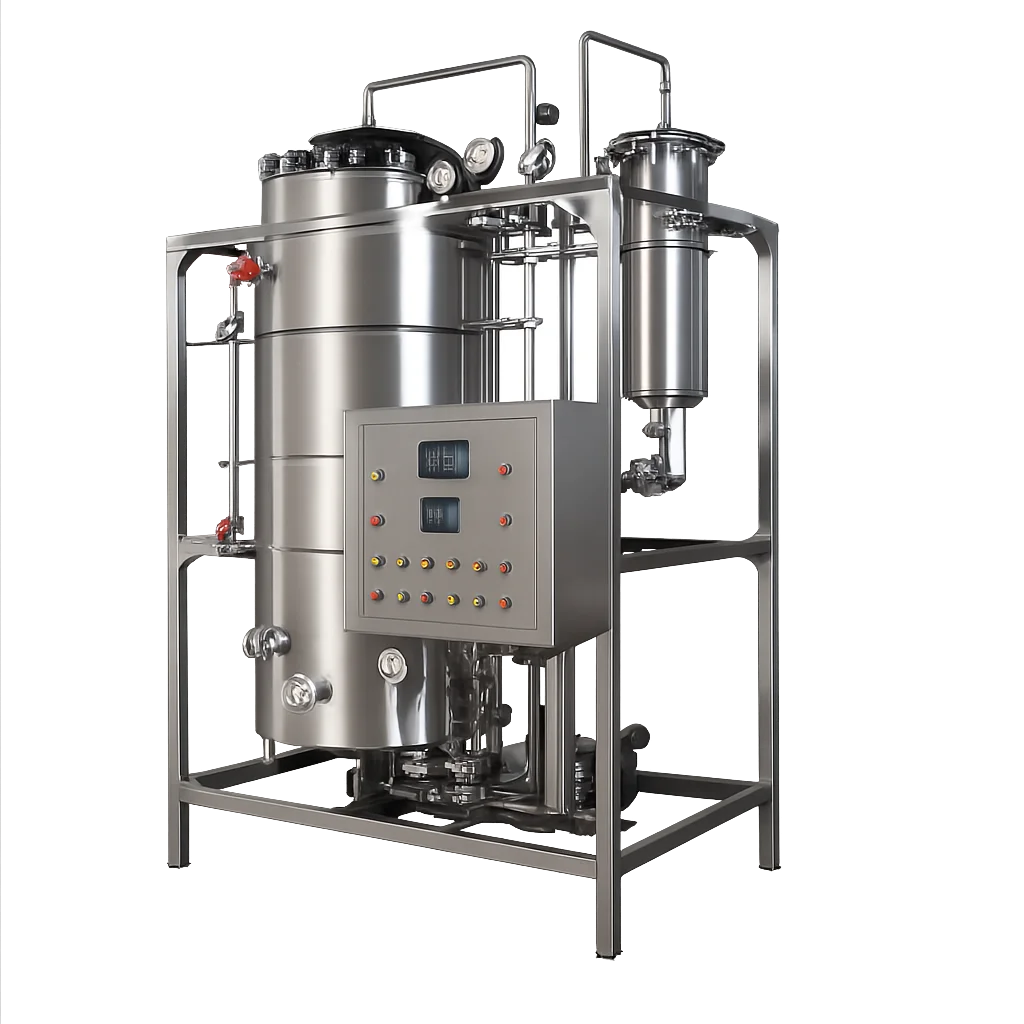
Features of Water Distillation Plant
Distillation Unit: Core component responsible for separating water from impurities through the process of vaporization and condensation.
Heat Source: Utilizes a heat source, often electric or steam-based, to vaporize water and leave impurities behind.
Condensation System: Consists of condensers to cool and convert the vapor back into liquid water, resulting in purified water.
Cooling Mechanism: Incorporates a cooling system to facilitate the condensation process efficiently.
Feedwater Inlet: Allows the introduction of raw or contaminated water into the distillation unit for purification.
Product Outlet: Provides an outlet for the purified water, ready for distribution or further treatment.
Waste or Concentrate Outlet: Disposes of the concentrated impurities or waste generated during the distillation process.
Monitoring Instruments: Includes instruments for monitoring temperature, pressure, and water quality to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Safety Features: Integrates safety mechanisms such as pressure relief valves and emergency shutdown systems to prevent accidents.
Material of Construction: Typically made of corrosion-resistant materials to withstand the water treatment process and ensure longevity.
Automated Controls: Modern water distillation plants often feature automated controls for efficient operation and to minimize human intervention.
Energy Efficiency Measures: Implements technologies like heat exchangers to enhance energy efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Multiple Effect Distillation (MED): Some advanced water distillation plants may use multiple-effect distillation for improved energy utilization.
Desalination Capability: In the case of desalination plants, additional features for removing salt from seawater may be included.
Environmental Compliance: Adheres to environmental regulations by incorporating systems to manage emissions and minimize environmental impact.
Routine Maintenance Access: Designed to facilitate routine maintenance tasks for the longevity and reliability of the plant.
Scaling Prevention Systems: Includes systems to prevent the buildup of scale and other deposits that may affect distillation efficiency.
Capacity: Variable capacity options to meet the specific needs of different applications and demand levels.
Quality Control Systems: Monitors water quality continuously and may include post-distillation treatment systems to meet specific purity standards.
Documentation and Reporting: Keeps records of operational parameters and may generate reports for regulatory compliance and performance analysis.
What is the fundamental purpose of a distillation plant?
Distillation plants are designed to separate different components in a mixture by exploiting variations in their boiling points, ensuring the production of purified substances.
How does distillation contribute to the production of essential oils?
Distillation, particularly steam distillation, is a common method for extracting essential oils from plants, capturing their aromatic and therapeutic properties.
Are all distillation plants the same, or do they vary based on industry needs?
Distillation plants vary significantly based on the industry’s specific requirements, with designs tailored to accommodate the unique characteristics of different substances.
What role does artificial intelligence play in modern distillation technology?
The integration of artificial intelligence in distillation technology aims to enhance efficiency, optimize processes, and contribute to sustainable practices.
How do distillation plants impact energy consumption in industrial processes?
Distillation plants can either contribute to energy efficiency by utilizing advanced technologies or pose challenges due to their energy-intensive nature; the balance depends on the specific design and implementation.
Can distillation plants be used for water purification?
Yes, distillation is an effective method for water purification, where contaminants are separated from water through the process of vaporization and condensation.
What safety precautions should be taken when operating a distillation plant?
Safety measures include strict adherence to regulatory standards, comprehensive employee training, and the development of robust emergency response plans to ensure a secure operating environment.
Are there any environmentally friendly practices associated with distillation plants?
Distillation plants can contribute to sustainability by ensuring the purity of products and exploring innovative technologies to minimize environmental impact, aligning with green practices.
What challenges do distillation plants face in terms of scaling issues?
Scaling issues, such as the accumulation of mineral deposits, can affect the efficiency of distillation plants. Regular maintenance and innovative solutions are essential to address these challenges.
How do distillation plants play a role in the petrochemical industry?
Distillation is a key process in the petrochemical industry, where crude oil is separated into different fractions, each with specific uses, ranging from fuels to various petrochemical products.
